コンプリート! loanable funds market graph 172396-Loanable funds market graph shifters
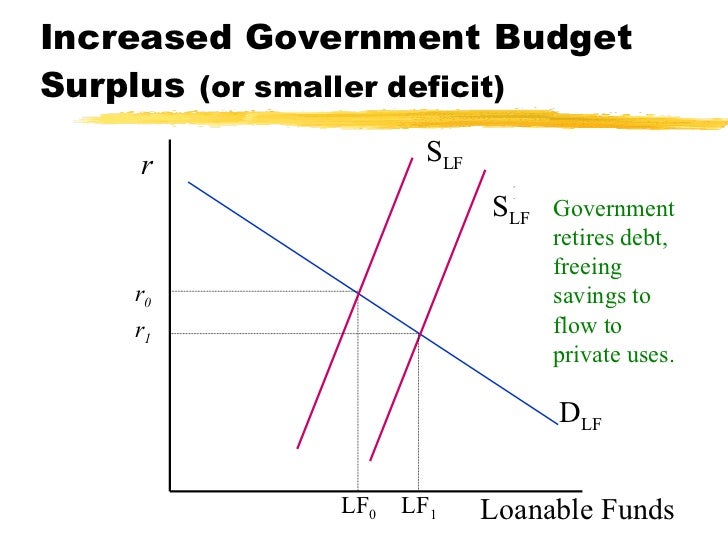
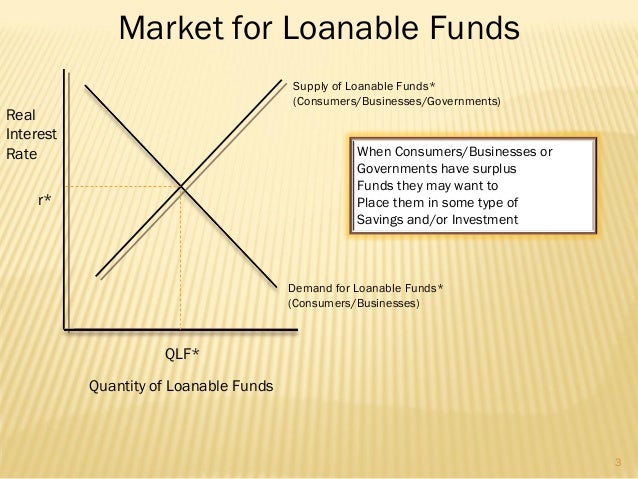
Loanable Funds Market Assumptions Households save but never borrow Firms and corporations borrow but never save Governments can save (in a budget surplus) and/or borrow (in a budget deficit), or be neutral ( in the case of a balanced budget) In a closed economy, firms and the government must borrowOk In this one I draw and explain the graph for loanable funds and crowding out To watch the loanable funds practice video please go to the Ultimate ReviewUpdate Once again I have updated this post with a few minor changes Notably, I have added to graphs illustrating a separate shift in supply and demand for loanable funds Based on discussions with readers via email, it appears that my previous graph illustrating in one diagram
1
Loanable funds market graph shifters
Loanable funds market graph shifters-A brief overview of the Loanable Funds Market, crowding out, and how it connects to the AD/AS graph Loanable Funds Market We use your LinkedIn profile and activity data to personalize ads and to show you more relevant ads



3 Supply And Demand For Loanable Funds The Following Chegg Com
Supply of Loanable Funds Shifters 1 The Savings Rate {direct} Consumer or corporate savings levels 2 Federal Reserve Lending {direct} Lending via discount window 3 Foreign Purchases of Domestic Assets {direct} International investments 4 Expectations For Future Economy {direct} Anticipation of economic performance Loanable funds market graph shifts Assuming loanable funds are all used for investment, loanable funds = investment Since an import quota reduces imports at any real exchange rate, net exports rise On the line graph, the demand for Shifting the supply of loanable funds reduces the total quantity at equilibrium, but also increases the real An equilibrium in the loanable fund market occurs when demand equals supply for loanable funds In a graph, equilibrium takes place at the point where the demand and supply curves intersect At this point, the equilibrium interest rate in the economy is determined
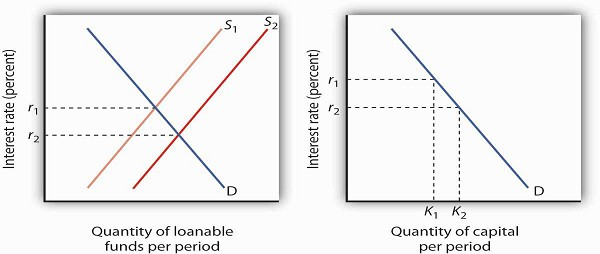
Panel (a) shows the result in the loanable funds market—a shift in the demand curve for loanable funds from D1 to D2 and an increase in the interest rate from r1 to r2 At r2, the quantity of capital demanded will be K2, as shown in Panel (b)MARKET FOR LOANABLE FUNDS – A free PowerPoint PPT presentation (displayed as a Flash slide show) on PowerShowcom id 7698MmE1N The market for loanable funds we will use a basic supply and demand graph to consumer/business borrowing because of govt Government deficit spending and the money market Does an increase in government spending without a corresponding if savings increases, supply of loanable funds shifts outward, increasing the reserves in banks, lowering real
The demand for loanable funds is also made up by those people who want to hoard it as idle cash balances to satisfy their desire for liquidity The demand for loanable funds for hoarding purpose is a decreasing function of the rate of interest At low rate of interest demand for loanable funds for hoarding will be more and viceversa 3Equation (p) shows that the supply of loanable funds depends on income and fiscal policy The demand for loanable funds depends on r Here r moves up or down to bring about equilibrium in the market for loanable funds The derived of the IS Curve We may now derive the IS curve from the equilibrium condition in the market for loanable funds We will use a basic Supply and Demand Graph to analyze this market The Market for Loanable Funds is NOT a real place It is a composite representation of



Changes In The Demand For Capital And The Loanable Funds Market Open Textbooks For Hong Kong



Changes In The Demand For Capital And The Loanable Funds Market Open Textbooks For Hong Kong
7 Draw a graph of the loanable funds market a shown in Visual 42 Point out the similarities between money and loanable funds and the graphs of the money and loanable funds market Point out that the vertical axis is the real interest rate in the loanable funds market and that the supply of loanable funds does depend on the interest rate 8The graph shows the US market for loanable funds (a)Draw a point at the market equilibrium Label it 1 Suppose that the US government finances its deficit by selling Treasury bills and bonds in the loanable funds market Draw a curve to show the effect of the government's action in the loanable funds market Label itTranscribed image text The following graph shows the market for loanable funds For each of the given scenarios, adjust the appropriate curve on the graph to help you complete the questions that follow Treat each scenario separately by resetting the graph to its original state before examining the effect of each individual scenario



Ap Macroeconomics Unit 4 Long Run Economic Growth And Loanable Funds Ppt Video Online Download



Worthwhile Canadian Initiative The Loanable Funds And Other Theories
Loanable funds market graph in recession Every graph used in ap macroeconomics The production possibilities curve model In this one i draw and explain the graph for loanable funds and crowding out Create your own flashcards or choose from millions created by other students The loanable funds market therefore recognizes the relationshipsAnswer the following questions regarding this graph a Explain why the supply of loanable funds is upward sloping b Explain why the demand of loanable funds is downward sloping c If the Federal Reserve sells government bonds, show what will happen to this graph Explain the effects on interest rates and the quantity of loanable funds d The Y axis on a loanable funds market is the real interest rate;




What Is The Relationship Between The Demand For Loanable Funds And Investment Economics Stack Exchange



Net Capital Outflow Wikiwand
On a correctly labeled graph of the loanable funds market in the United States, illustrate the effect of this influx of FDI QUANTITY (loanable funds) US Loanable Funds Market REAL INTEREST RATE S D S1 QIf r1 r QIf1 11reat Britain was a leading investor in American firms at this time Use correctly labeled graphs of GIn this video, learn how the demand of loanable funds and the supply of loanable funds interact to determine real interest rates This is the currently selected itemThe graph shows the loanable funds market when there is neither a government budget surplus nor a government budget deficit Draw a point at the equilibrium quantity of loanable funds and the equilibrium real interest rate Label it 1 Now suppose that the government has a



A In The Loanable Funds Market Graph See Chegg Com




Money Market And Loanable Funds Two Day Unit Money Market Money Supply Vertical Vs Money Demanded Downward Sloping X Axis Quantity Of Money Y Axis Ppt Download
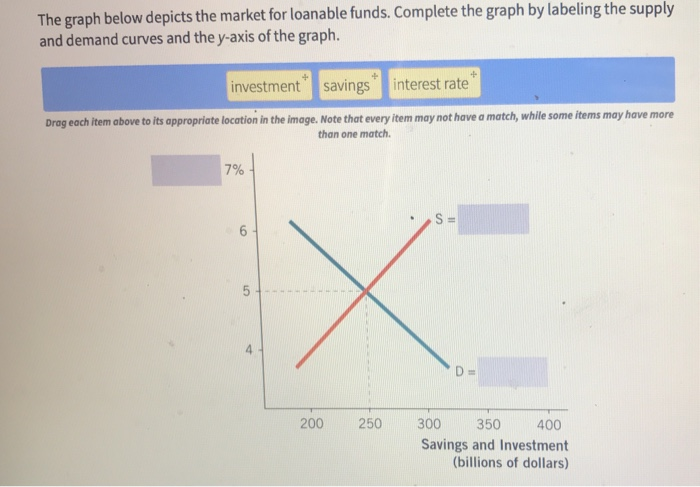
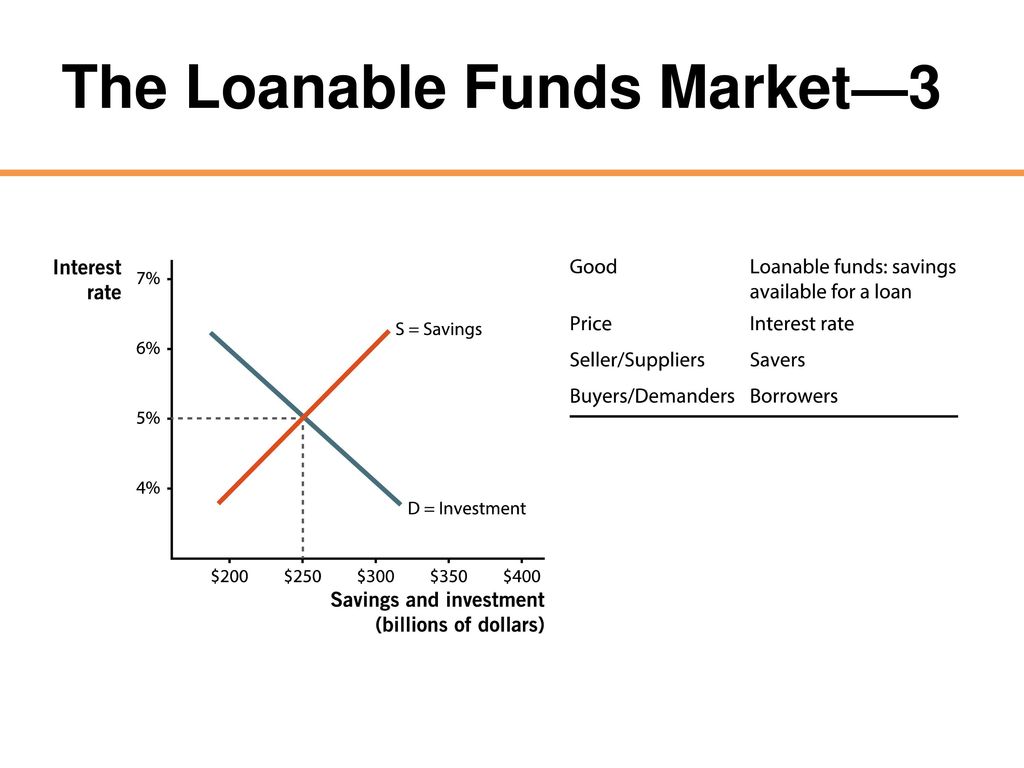
Loanable funds The term loanable funds is used to describe funds that are available for borrowing Loanable funds consist of household savings and/or bank loans Because investment in new capital goods is frequently made with loanable funds, the demand and supply of capital is often discussed in terms of the demand and supply of loanable funds(0,800) Middle (400, 4) _____ is the source of the supply of loanable fundsLoanable fund market is a market Market of orange Loanable fund market Good Oranges Loanable funds Suppliers Farmers Savers, such as households Demander s Grocery shoppers Borrowers, such as firms Price Price of orange Interest rate ____Interest rate_____ is the price of loanable fund 2



Http Www Socsci Uci Edu Mouyang Ps b Answer key4 Pdf




Foreign Exchange Markets Impact On The Loanable Funds And Money Market Graphs Youtube
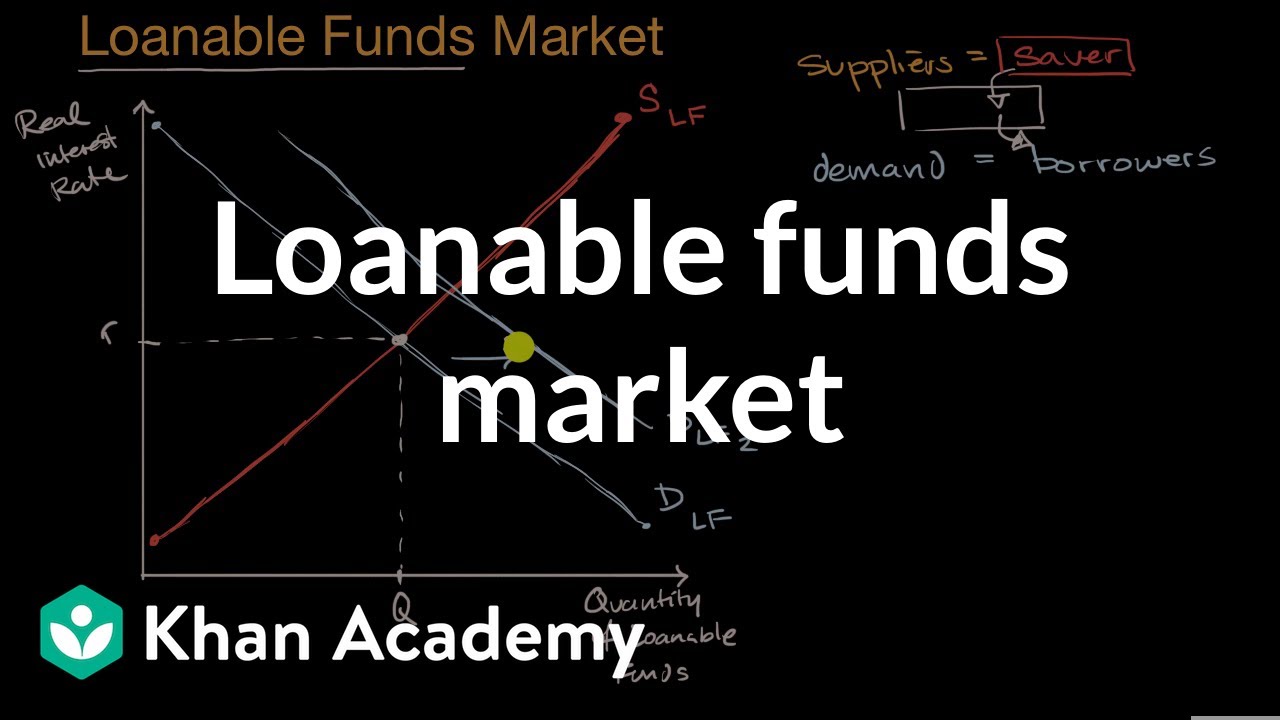
The Market for loanable funds Loanable funds market National savings and investment Lesson summary the market for loanable funds Practice The market for loanable funds This is the currently selected item Practice Changes in the market for loanable funds Lesson summary the market for loanable funds Changes in the market for loanableThe real interest rate is associated with the loanable funds marketThe nominal interest rate is associated with the money market In the long run, more investment spending will cause the long run aggregate supply curve to increase as wellAbbreviated with a lower case "r" That means it is the nominal interest rate minus inflation It is price for taking out a loan The X axis is the quantity of loanable funds The supply curve is the savings supply and the demand curve is predominantly the demand for investments




The Loanable Funds Market And Crowding Out Macro Topic 4 7 Youtube
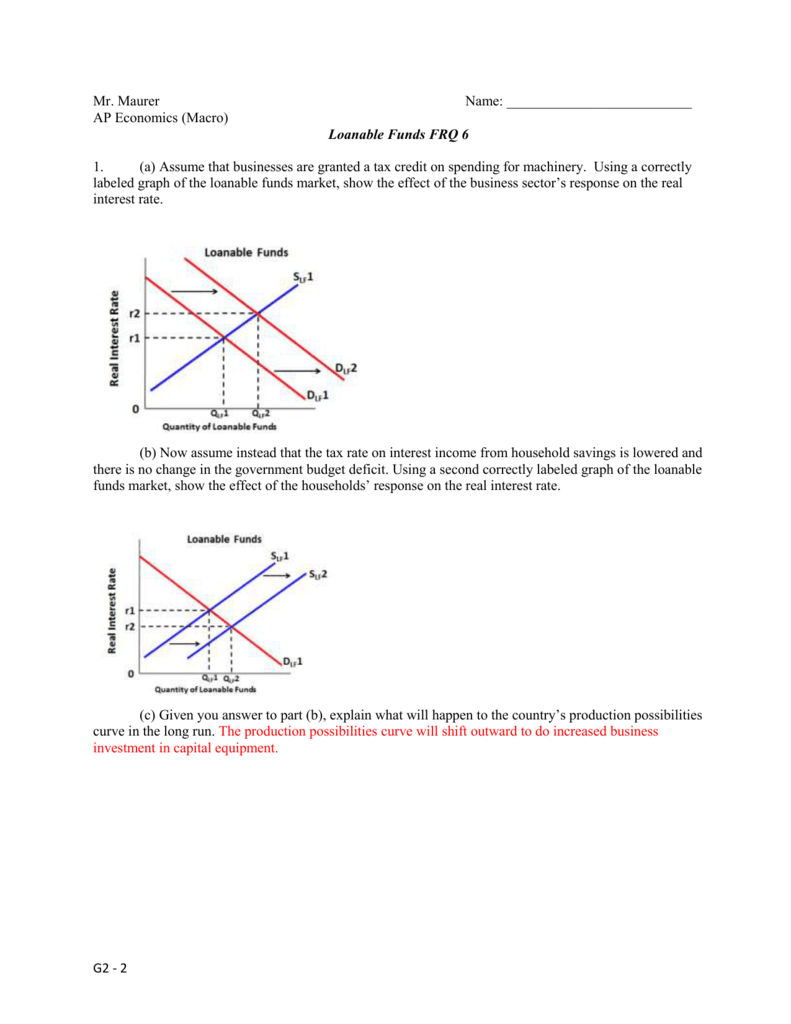



Mr Maurer Name Ap Economics Macro Loanable Funds Frq 6 1
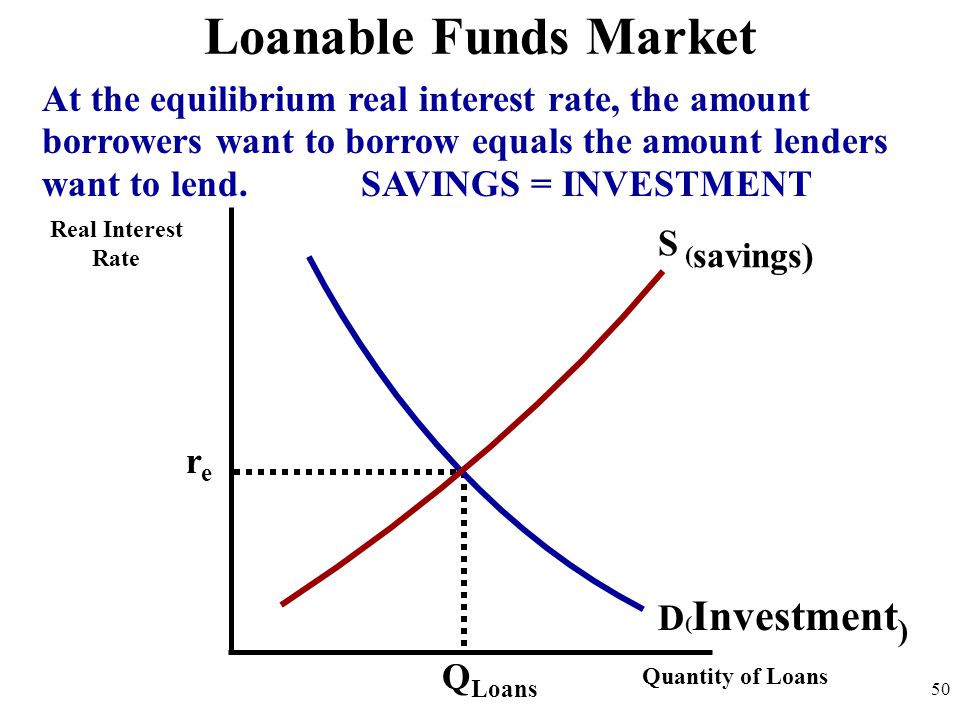
The loanable funds market illustrates the interaction of borrowers and savers in the economy It is a variation of a market model, but what is being "bought" and "sold" is money that has been saved Borrowers demand loanable funds and savers supply loanable funds The market is in equilibrium when the real interest rate has adjusted so In the market for loanable funds!Loanable Funds vs Money Market whats the difference?




The Following Graph Shows The Market For Loanable Funds In A Closed Economy The Upward Sloping Orange Homeworklib



1
Loanable Funds Market Worksheet 2 Draw a graph of the loanable funds market showing the effect of each of the following on the real interest rate and quantity of loanable funds Labeling the change with either (Dlf1) or (Slf1), (rir1) and (Qlf1) 1 TheQuestion 4 Supply and demand for loanable funds The following graph shows the market for loanable funds in a closed economy The upwardsloping orange fine represents the supply of lanabil funds, and the downward sloping blue line represents the demand for loanable funds Supply INTEREST RATE (Percent Demand 700 0 10 000 460 500 100Loanable Funds Market Part I 1 Draw a correctly labeled graph showing equilibrium in the loanable funds market 2 Does each of the following affect either the supply or the demand for loanable funds, and if so, does the affected curve increase (shift




Loanable Funds Market Graph



Solved 1 Let S Think About The Market For Loanable Funds One Of Its Examples Is The Market For Housing Loans Let S Analyze How Covid 19 Affects Course Hero
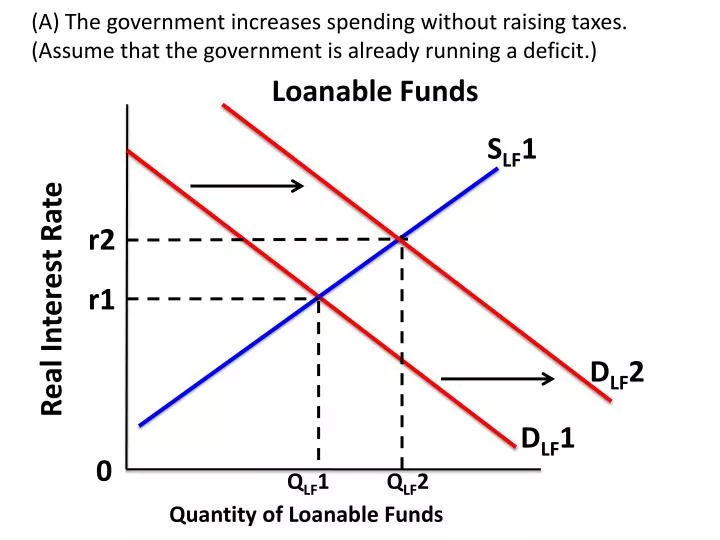
Draw a graph Of the loanable funds market showing the effect of each of the following on the real interest rate and quantity of loanable funds (A) The government increases spending ceteris paribus (B) The government increases tax on income from interest payments33 Firms care about their aftertax rate of return on investment projects In the market for loanable funds, graph and explain the effect of an increase in taxes on business profits The loanable funds theory analyzes the ideal interest rate with a linear regression in which the quantity of loanable funds is plotted on the X axis and the real interest rate is plotted on the Y axis Then, two data sets form two lines on the graph demand for loanable funds and supply for loanable funds Where these two lines intersect is the equilibrium interest rate, or the ideal




Macroeconomics Graphs Ap Economics Mr Bordelon Simple Circular
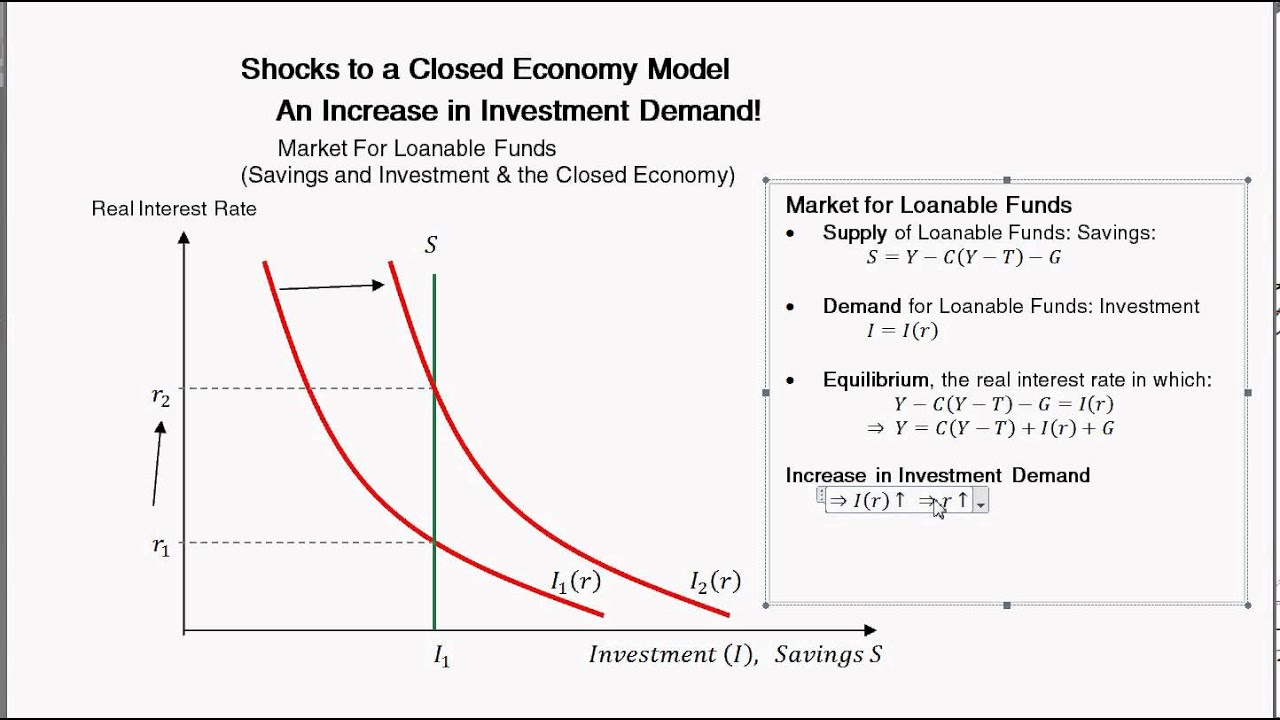



Change In Investment Demand And The Loanable Funds Market Intermediate Macroeconomics Youtube
The Markets for Money and Loanable Funds In the first section, Eric Dodge walks users through the graphs for money and loanable funds markets With the support of these materials, facilitators on any level will want to stress when to use the money market graph rather than the loanable funds5 Graph Drawing Drills for the Loanable Funds Market Below you will find 5 questions with explanations to help you quickly review how to draw and manipulate the Loanable Funds market graph To learn more about the Loanable Funds market, head to the Loanable Funds content review page To practice more, check out the Loanable Funds review game Tutorial on the loanable funds graph, change in real interest rates



The Loanable Funds Market Principles Of Economics Scarcity And Social Provisioning 2nd Ed



1
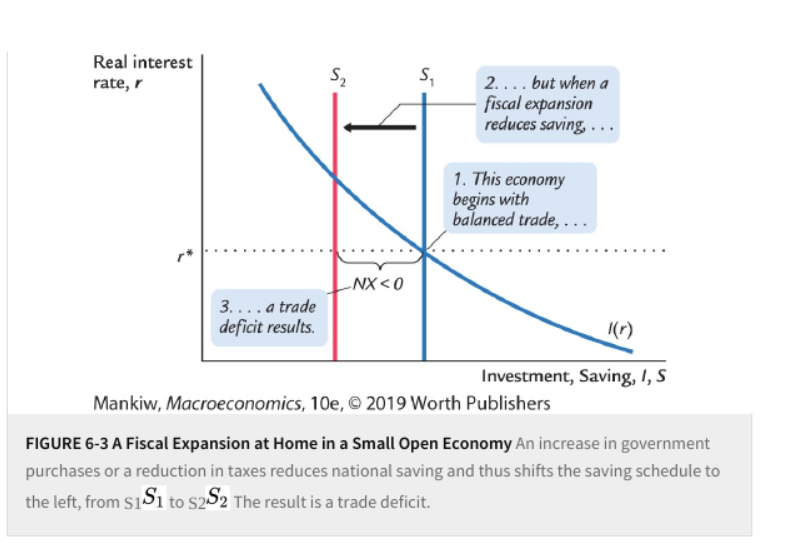
Consequently, is the interest rate in the loanable funds market nominal or real?When the money supply increases, the supply of loanable funds increases Thus, the interest rate will decrease(a) Using a correctly labeled graph of the loanable funds market, show how a decision by households to increase savings for retirement will affect the real market interest rate in the short run (b) Suppose the nominal interest rate has been 6 percent with no expected inflation If inflation is now expected



Alex J Relating The Money Market Loanable Funds Market And Ad As



1
The nominal interest rate found on the money market graph as well as the real interest rate found on the loanable funds market graph impact the price of bonds Interest rates and bond prices are inversely related so as interest rates rise, bond prices fall and vise versa To understand why, take an example of a bond that originally sold forThe following graph shows the market for loanable funds For each of the given scenarios, adjust the appropriate curve on the graph to help you complete the questions that follow Treat each scenario separately by resetting the graph to its original state before examining the effect of each Individual scenarioThe graph shows the market for loanable funds Show the effect of an increase in government borrowing by shifting the proper curve What is the effect of this change on the interest rate?




The Market For Loanable Funds Model Article Khan Academy



What To Know About Loanable Funds By Test Day Reviewecon Com
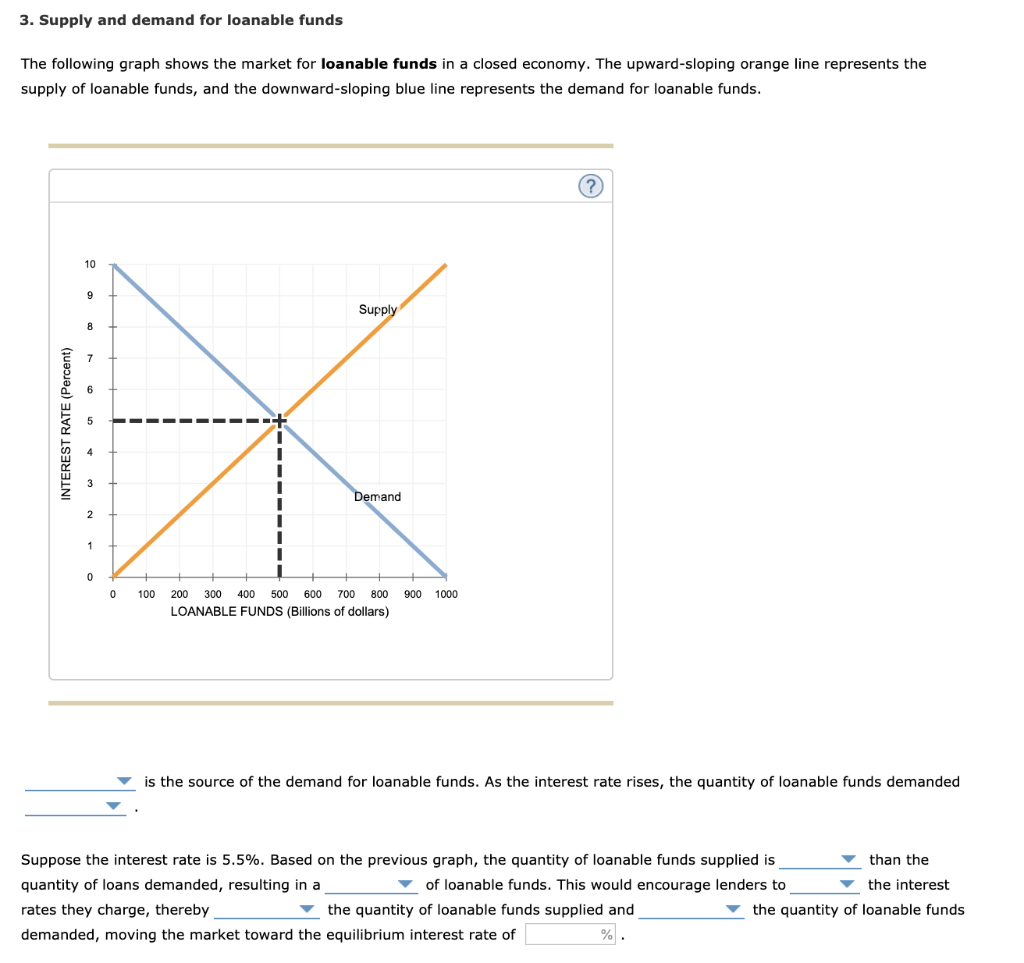
The loanable funds market describes the behavior of savers and borrowers The market for loanable funds is a way of representing all of the potential savers and all of the potential borrowers in an economy It has the same features of other markets that weThe following graph shows the market for loanable funds in a closed economy The upwardsloping orange line represents the supply of loanable funds, and the downwardsloping blue line represents the demand for loanable funds Supply (0,0);How much does the quantity of loanable funds supplied increase with the increase in the interest rate from i 1 to i 2?



Definition Of Loanable Funds Model Higher Rock Education




Unit 4 Money Banking And Monetary Policy Copyright
Money Market vs Loanable funds Market This market refers to the Money Supply (M1 and M2) The Money Supply curve is vertical because it is determined by the Fed's (or central bank's) particular monetary policy On the X axis is the Quantity of money supplied and demanded, and on the Y axis is the nominal interest rate A tight monetaryAccording to the loanablefunds theory, the rate of interest is determined by the demand for and the supply of funds in the economy at that level at which the two (demand and supply) are equated Thus, it is a standard demandsupply theory as applied to the market for loanable funds (credit), treating the rate of interest as the price (per unit




Crowding Out Effect On Loanable Funds Graph



Loanable Funds




Monetary Policy On The Loanable Funds As Ad Graphs Youtube



Www Dentonisd Org Cms Lib Tx Centricity Domain 929 Loanable Funds Market Mcfarling Fall 11 Pdf Pdf



Solved A Draw A Graph Representing A Loanable Funds Market Assume Inelastic Supply Of Loanable Funds Make Sure To Label Axes Curves And Equili Course Hero



Www Tamdistrict Org Cms Lib Ca Centricity Domain 1076 Loanable funds practice quiz Pdf



The Market For Loanable Funds



Economics In Plain English Loanable Funds Vs Money Market What S The Difference



Apcentral Collegeboard Org Pdf Ap19 Apc Macroeconomics Q3 Set 1 Pdf



Economics In Plain English A Closer Look At The Crowding Out Effect



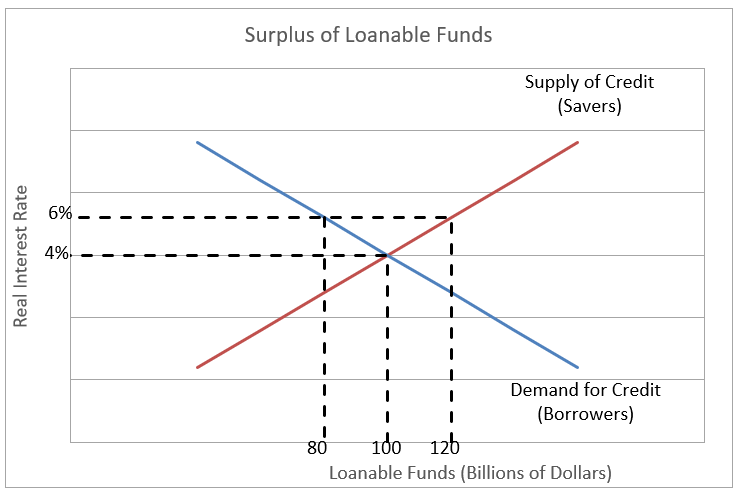
The Graph Below Depicts The Market For Loanable Chegg Com
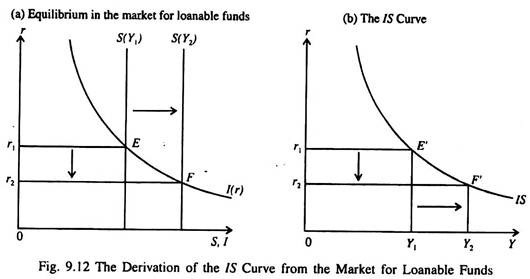



Loanable Funds Interpretation Of The Is Curve With Diagram



Loanable Funds Policonomics




The Graph Shows The Market For Loanable Funds Draw A Point At The Market Equilibrium Label It 1 Suppose That The Brazilian Government Borrows The Requited Funds In The Loanable Funds Market




Using A Graph Representing The Market For Loanable Funds Show And Explain What Happens To Interest Homeworklib
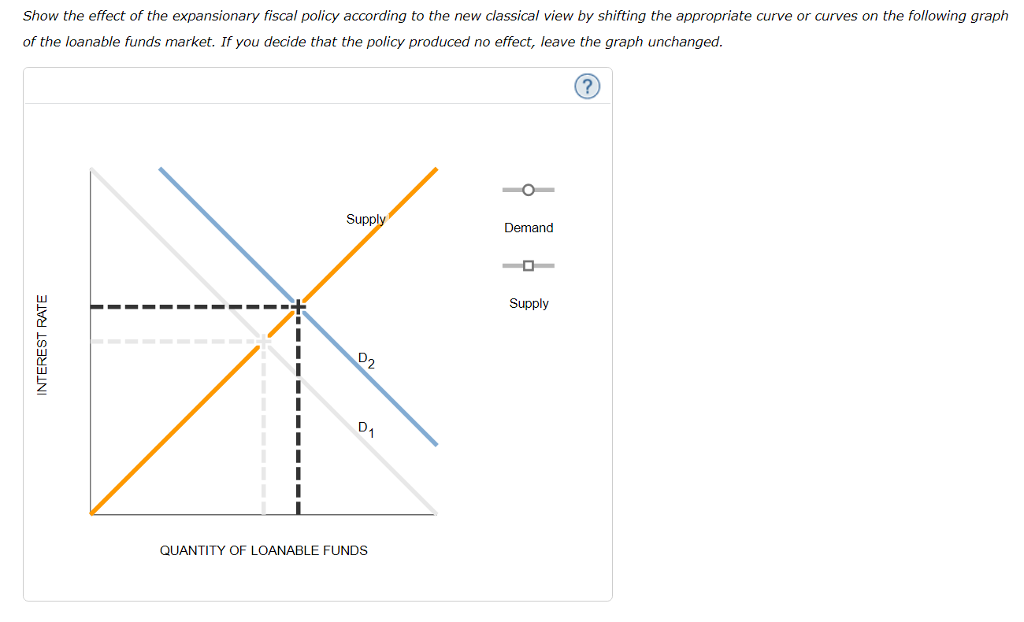



5 New Classical View Suppose Chegg Com




The Market For Loanable Funds Model Article Khan Academy



Nanopdf Com Download Chapter 23 5aea23cde5c55 Pdf



Economics In Plain English Loanable Funds Vs Money Market What S The Difference




Keynesian Consumption Loanable Funds Mps Mpc Ap Babbitt Notes




The Weekend Quiz April 28 29 18 Answers And Discussion Bill Mitchell Modern Monetary Theory



Changes In The Demand For Capital And The Loanable Funds Market Open Textbooks For Hong Kong




Activator Chapter 26 What Would Be The Disadvantage Of Putting Your Savings Under Your Mattress List Some Places That You Could Invest Your Money That Ppt Download




Loanable Funds
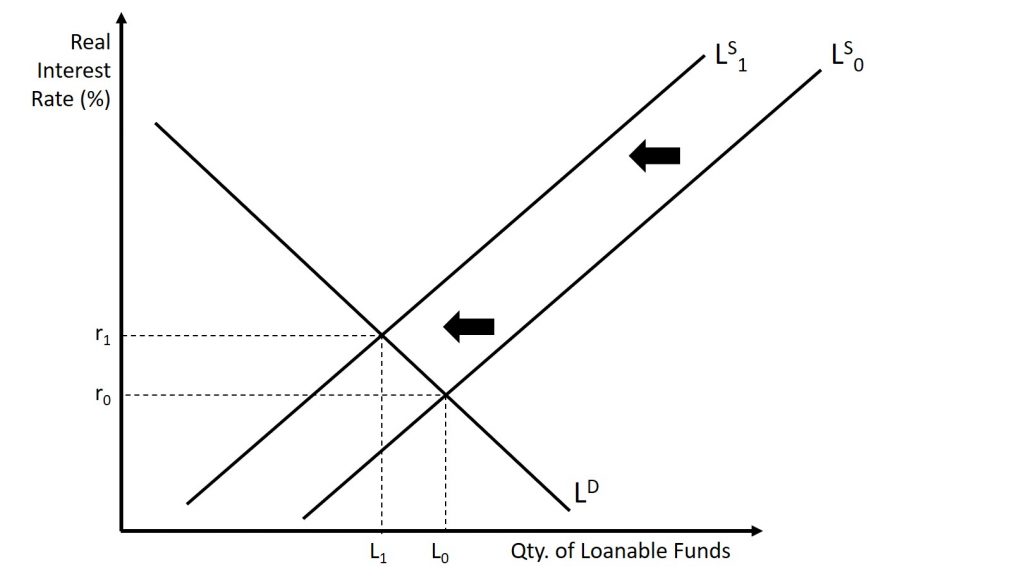



The Market For Loanable Funds Introduction To Macroeconomics



Ppt Loanable Funds Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




Ap Econ 5 29 The Market For Loanable Funds Flashcards Quizlet
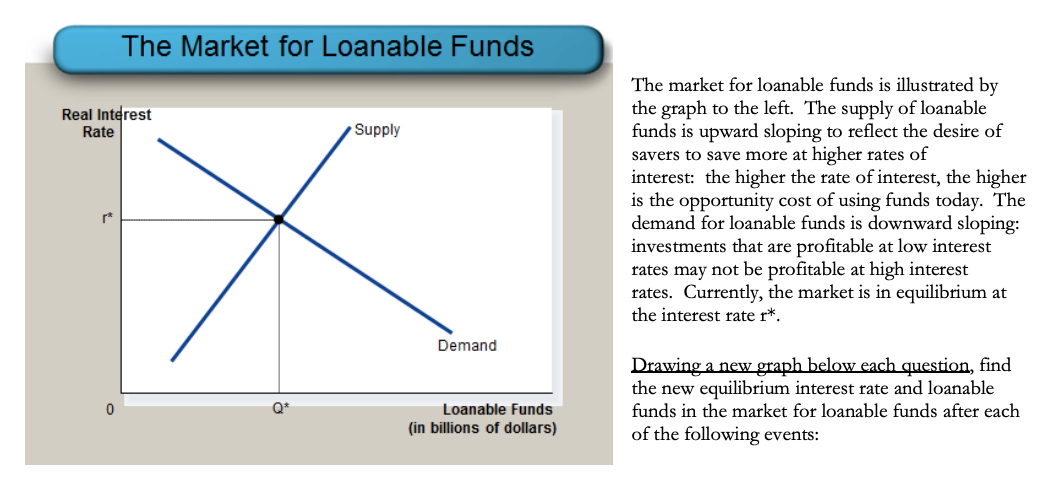



The Market For Loanable Funds Real Interest Rate Chegg Com




The Market For Loanable Funds Model Article Khan Academy




3 Supply And Demand For Loanable Funds The Following Chegg Com




Effects Of An Expected Increase In The Inflation Rate On The Market For Loanable Funds Economics Stack Exchange
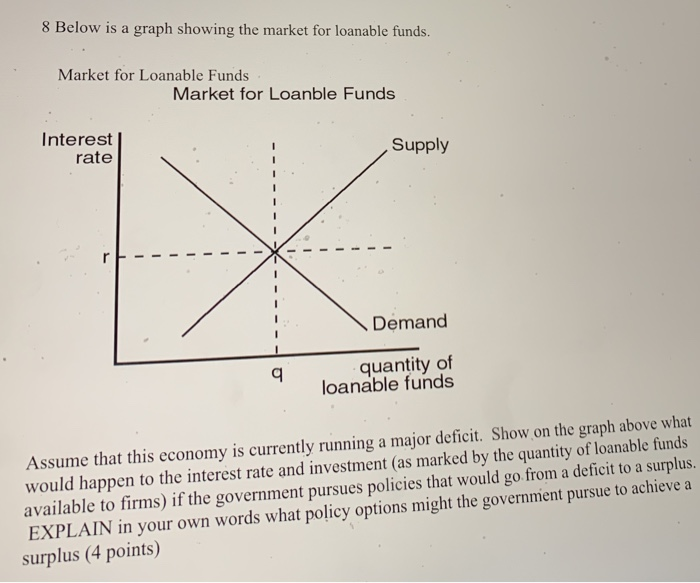



8 Below Is A Graph Showing The Market For Loanable Chegg Com
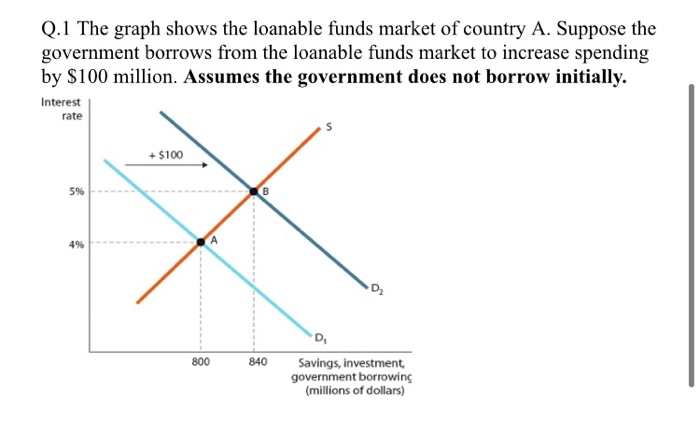



Q 1 The Graph Shows The Loanable Funds Market Of Chegg Com




Reading Loanable Funds Macroeconomics




Capital Loanable Funds Interest Rate



Economics In Plain English Loanable Funds Vs Money Market What S The Difference




A The Government Increases Spending Without Raising Taxes Assume That The Government Is Already Running A Deficit Loanable Funds D Lf 2 Real Interest Ppt Download




Shifting The Demand Curve For Loanable Funds Youtube



Macroeconomics Loanable No Bull Economics Lessons



Worthwhile Canadian Initiative The Loanable Funds And Other Theories
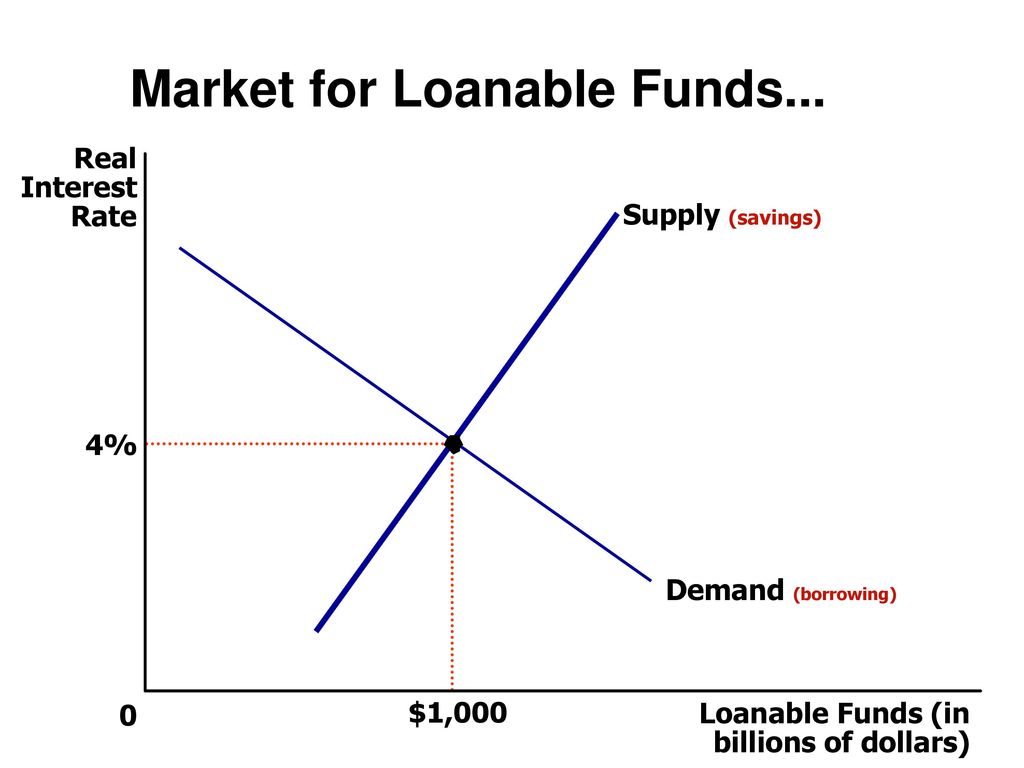



Loanable Funds Market Module Ppt Download




A The Government Increases Spending Without Raising Taxes Assume That The Government Is Already Running A Deficit Loanable Funds D Lf 2 Real Interest Ppt Download




The Graph Given Below Shows The Market For Loanable Funds In A Closed Economy The Upward Sloping Orange Line Represents The Supply Of Loanable Funds And The Downward Sloping Blue Line Represents The Demand
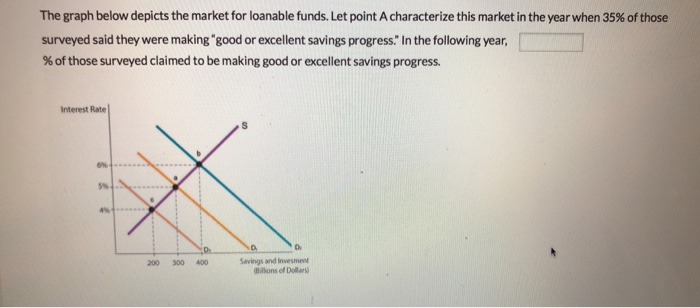



The Graph Below Depicts The Market For Loanable Chegg Com




Loanable Funds Able Funds Demand Shifters Changes In




Interest Rates And Loanable Funds




The Following Graph Shows The Market For Loanable Chegg Com
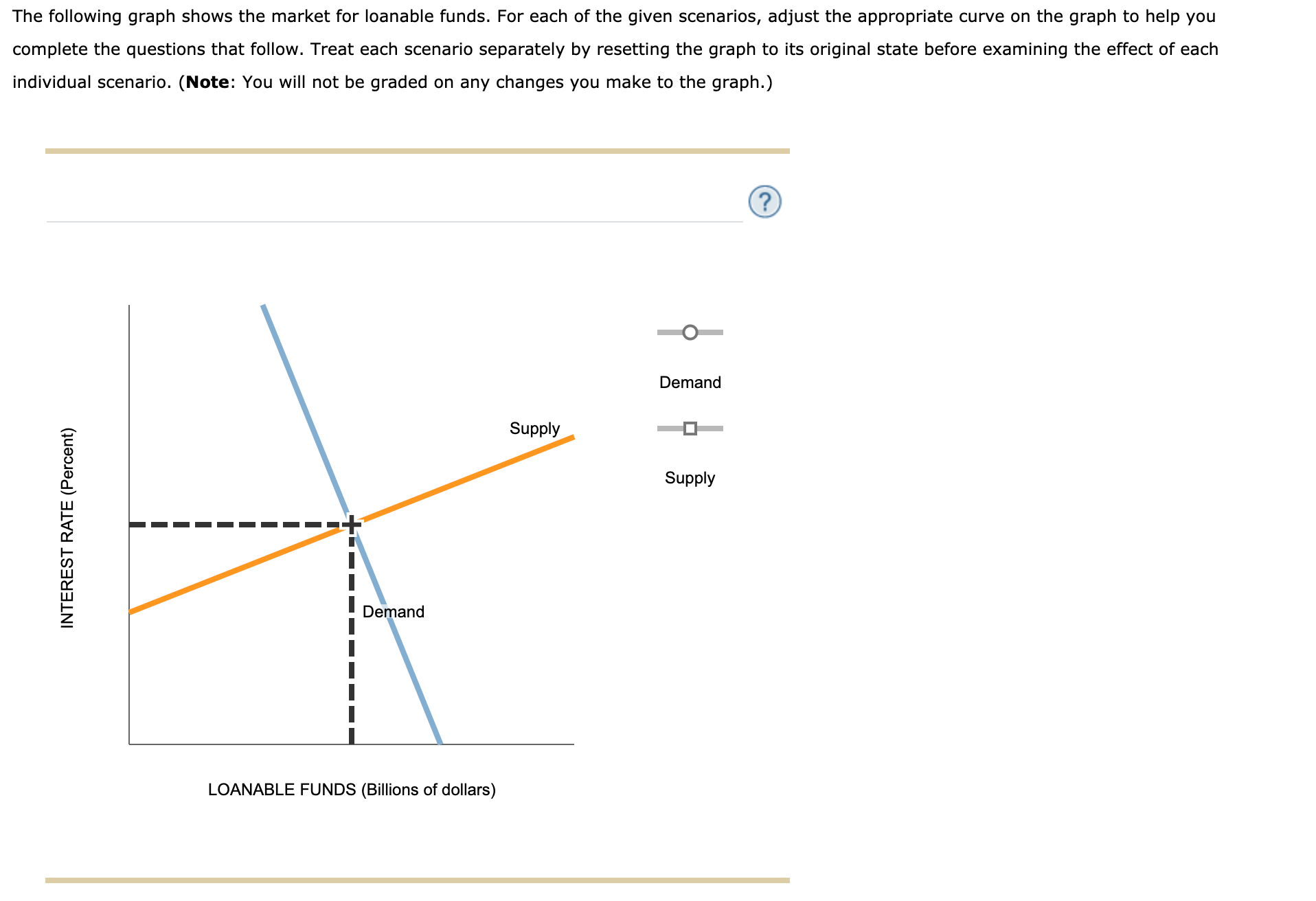



Answered The Following Graph Shows The Market Bartleby




Effect Of Lower Government Spending On Loanable Funds Market Economics Stack Exchange



1



The Market For Loanable Funds Course Hero



Loanable Funds V Market What S The Difference Investing Post



Market For Loanable Funds




As The United States Economy Moves Out Of A Recession U S Financial Investors Increase Their Purchases Of Stocks That Are Expected To Earn A Higher Rate Of Return Than They Are Currently




The Market For Loanable Funds Supply Demand Loanable Funds Demand Curve Slope Demand For Loanable Funds D The Loanable Funds Demand Curve Is Downward Ppt Download



Loanable Funds Market Video Khan Academy



Savings Interest Rates And The Market For Loanable Funds Ppt Download




Ch 12 Aggregate Demand And Aggregate Supply Lynn S Blog
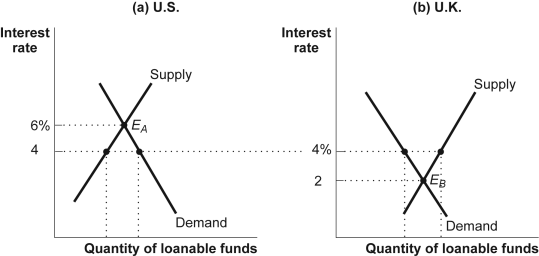



1 The Figure Shows The Loanable Funds Market For Two Chegg Com
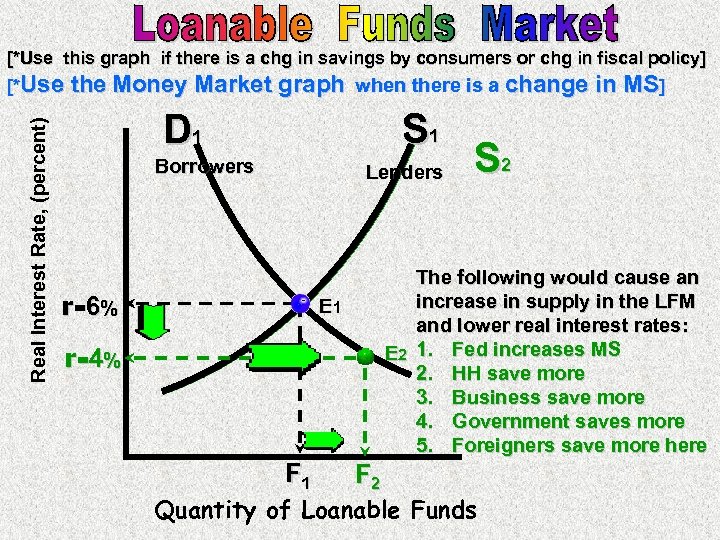



Primer Before Taking The 05 Macro Mc Exam
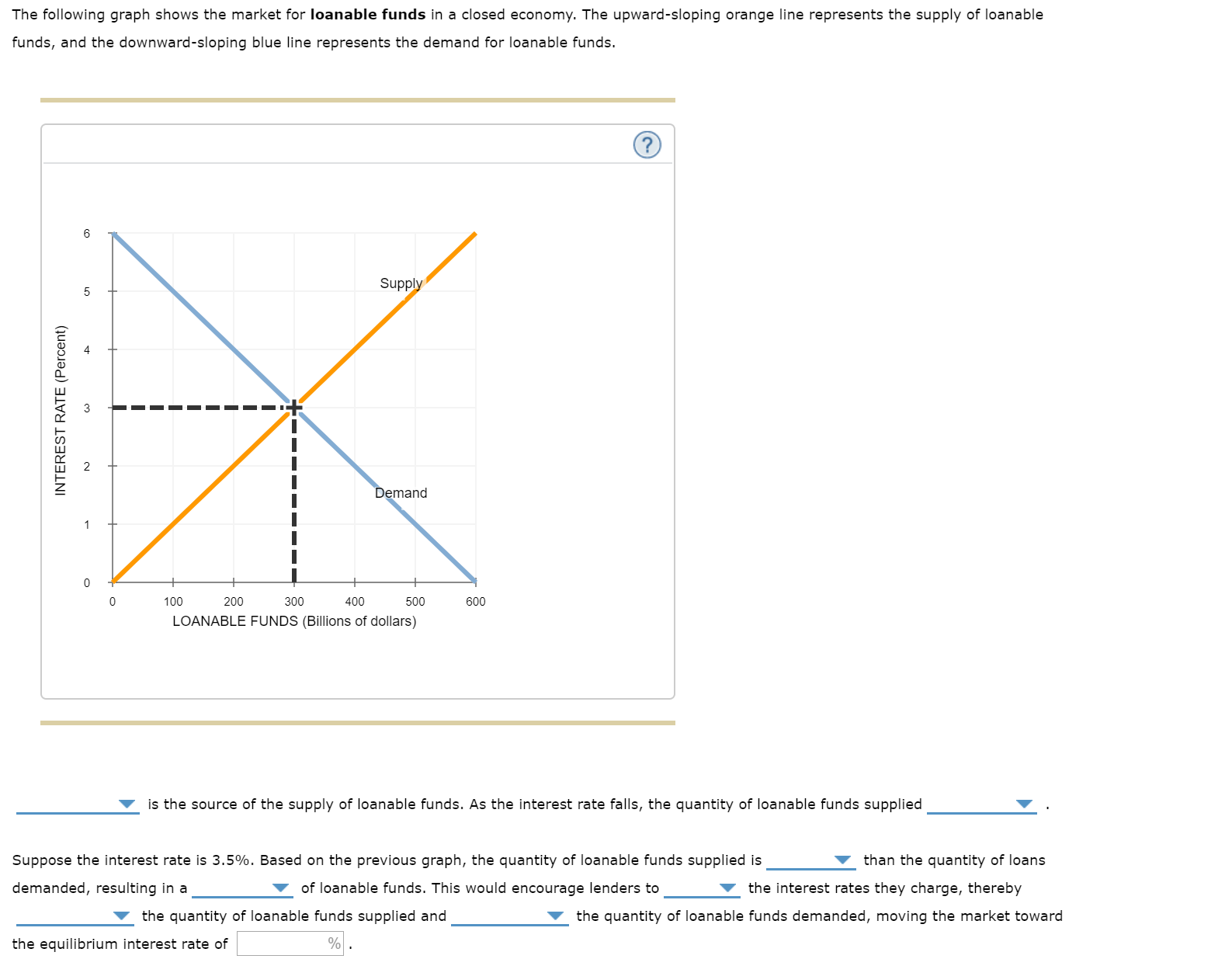



Answered The Following Graph Shows The Market Bartleby
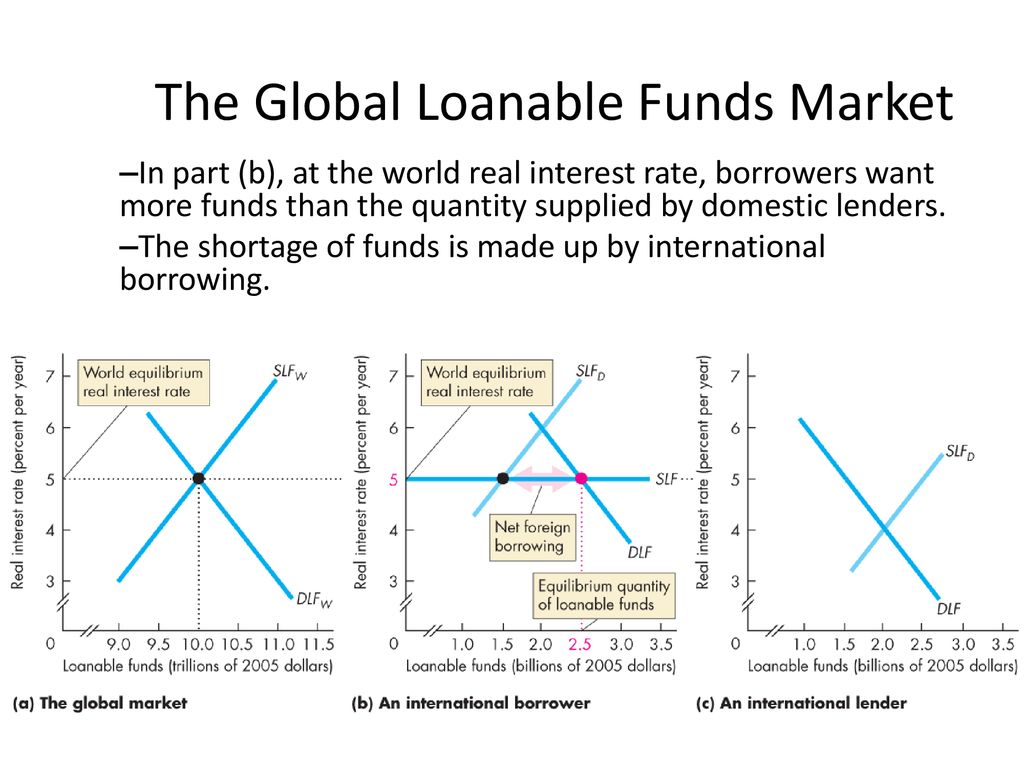



The Global Loanable Funds Market Ppt Download




Redelsheimers Graphs To Know Ap Macro Review Copyright




Econowaugh Ap Nominal Vs Real Money Supply Vs Loanable Funds




The Market Of Loanable Funds With An Example Of Crowding Out Freeeconhelp Com Learning Economics Solved




Reading Loanable Funds Macroeconomics




The Natural Interest Rate Fallacy Why Negative Interest Rate Policy May Worsen Keynesian Unemployment 1



Market For Loanable Funds Activity



Www Palmislandtraders Com Econ53 Chap3 Pdf



Www Palmislandtraders Com Econ53 Chap3 Pdf



Www Palmislandtraders Com Econ53 Chap3 Pdf



Loanable Funds Policonomics
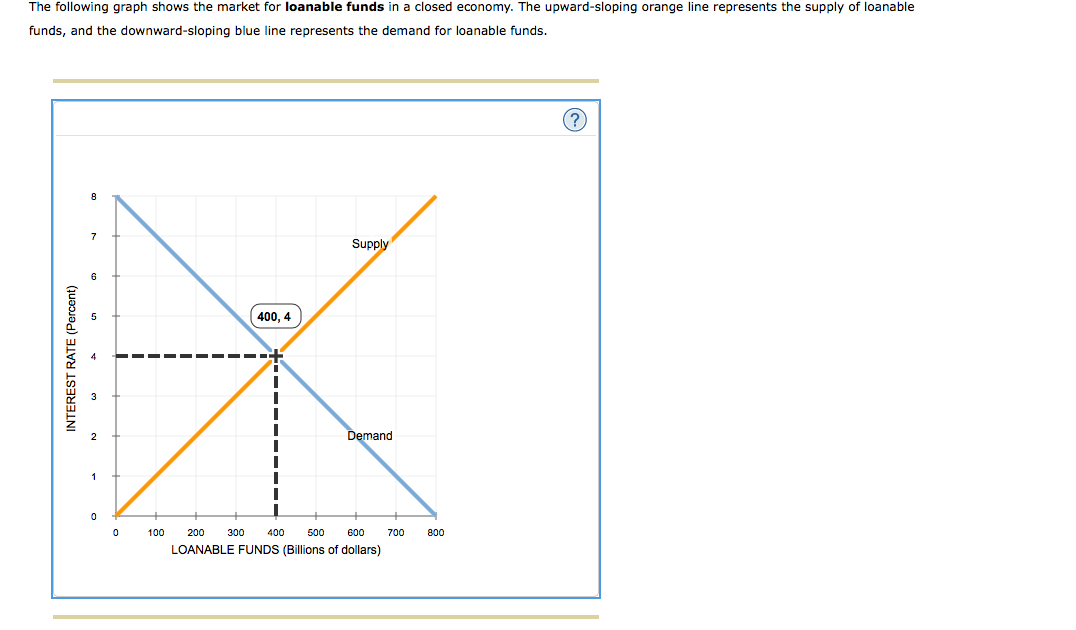



Answered Is The Source Of The Demand For Bartleby
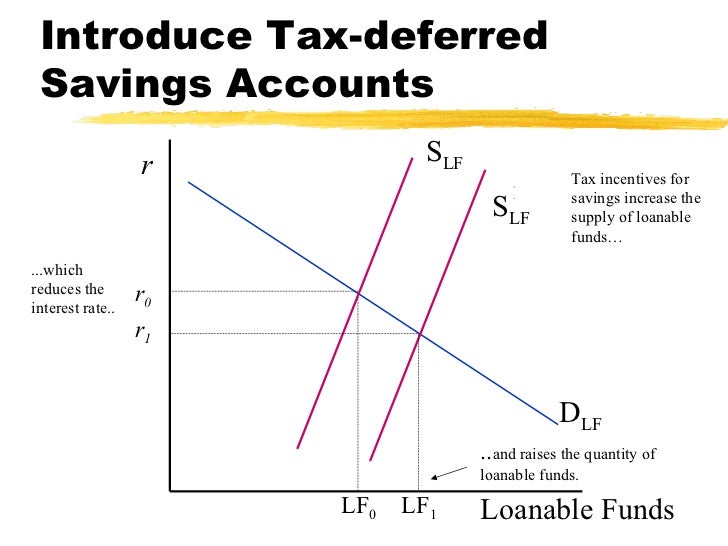



Loanable Funds




Use The Graph Of The Loanable Funds Market Below If Chegg Com



Www Birdvilleschools Net Cms Lib Tx Centricity Domain 4466 Unit 5 exam review key Pdf




Solved 5 The Market For Loanable Funds And Government Policy The 1 Answer Transtutors



Worthwhile Canadian Initiative The Loanable Funds And Other Theories


コメント
コメントを投稿